Table of Contents
What Is IoT in Healthcare?
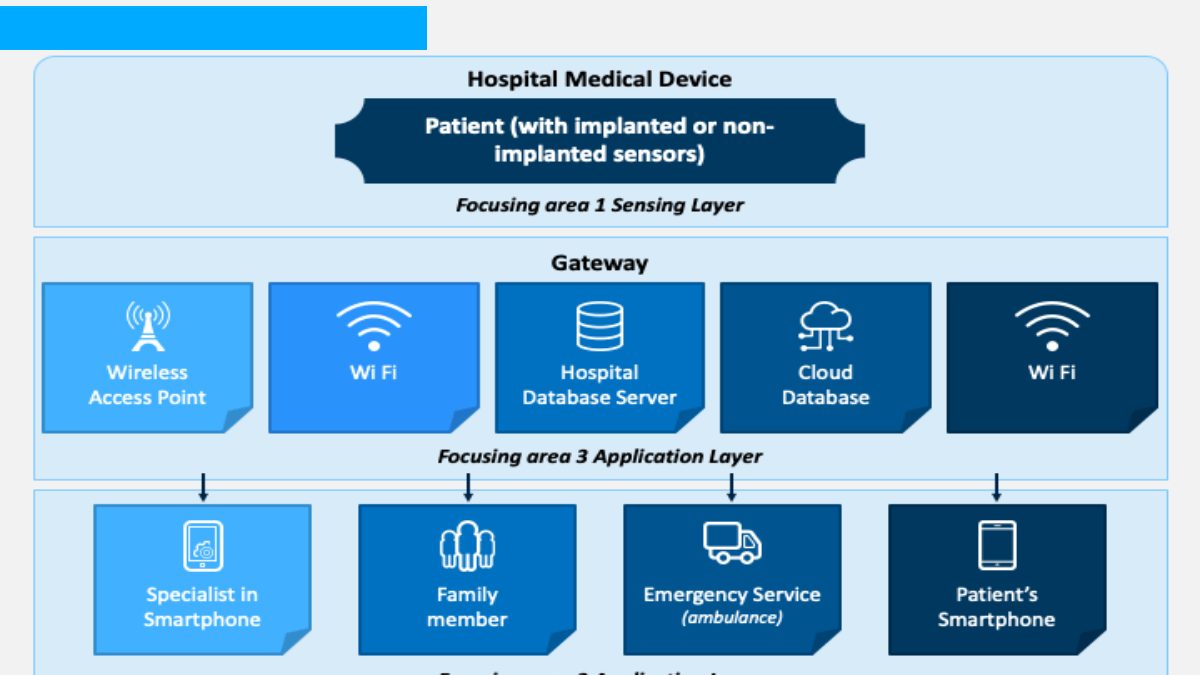
The Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare refers to a system of interconnected medical devices, sensors, software, and cloud platforms that collect, share, and analyze patient data in real time. These connected systems help hospitals, clinics, and home-care providers improve diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment efficiency.
IoT in healthcare makes traditional medical processes more accurate and automated. Devices like wearables, smart beds, infusion pumps, and remote monitoring tools continuously gather patient data and transmit it to healthcare providers. This leads to faster decision-making, early disease detection, and improved patient outcomes.
In simple terms, IoT transforms healthcare into a more intelligent, data-driven, and patient-centric ecosystem.
Key IoT Devices Used in Hospitals and Clinics
Healthcare IoT relies on a variety of connected medical devices, each designed for a specific purpose. Some of the most widely used IoT devices in modern medical environments include:
Wearable Health Trackers
Devices such as smartwatches, fitness bands, and ECG patches monitor vitals like heart rate, oxygen levels, movement, sleep patterns, and blood pressure.
Remote Patient Monitoring Devices
These include smart glucometers, connected blood pressure cuffs, digital thermometers, pulse oximeters, and other at-home diagnostic tools that send real-time data to healthcare providers.
Smart Hospital Equipment
Many hospitals now use IoT-enabled tools such as:
-
Smart infusion pumps
-
Connected ventilators
-
Smart beds that track movement, posture, and patient vitals
-
Asset tracking tags for medical equipment
Implantable Medical Devices
Pacemakers, insulin pumps, and neuro-stimulators equipped with IoT connectivity improve treatment precision and allow physicians to tune settings remotely.
Top IoT Healthcare Use Cases (Monitoring, Wearables, Smart Beds, etc.)
IoT in healthcare supports a broad range of applications that benefit patients, caregivers, and medical staff. Some of the leading use cases include:
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Patients with chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, and asthma can be monitored 24/7 using connected devices. Doctors receive continuous data, enabling proactive care.
Smart Wearables for Fitness and Preventive Health
Wearables monitor physical movement, sleep, heart rate variability, and stress levels. These help users track their well-being and enable doctors to identify early health risks.
Smart Hospital Management
IoT supports automation and efficiency in hospitals through:
-
Smart beds with pressure sensors to prevent bedsores
-
Automated medicine dispensing systems
-
Real-time patient tracking
-
Predictive maintenance of machines
Emergency Response and Ambulance IoT
Connected ambulances send patient data (ECG, blood pressure, vitals) to hospitals before arrival, reducing treatment delays.
IoT in Elderly Care
IoT devices such as fall detectors, motion sensors, and medication reminders help seniors live safely at home.
Connected Imaging and Diagnostics
MRI, X-ray, and CT scan machines integrated with IoT generate high-quality images and send data to cloud systems for fast analysis.
Benefits and Risks of IoT in Healthcare
Key Benefits
-
Real-time monitoring of patient vitals
-
Early diagnosis through continuous data tracking
-
Reduced hospital visits with remote care
-
Better decision-making through analytics
-
Improved hospital workflows and reduced errors
-
Cost savings for both patients and healthcare providers
Key Risks
-
Cybersecurity threats if devices are not encrypted
-
Data privacy concerns with cloud storage
-
Device malfunction risks during critical care
-
Integration challenges between different IoT systems
Hospitals must implement strong security protocols, regular updates, and device audits to ensure safe IoT deployment.
Simple IoT in Healthcare PPT Outline for Students
Below is a clean, reusable PPT structure you can copy directly into slides:
Slide 1: Title Slide
-
IoT in Healthcare
-
Definition + short intro
Slide 2: What Is IoT in Healthcare?
-
Meaning
-
How IoT works
-
Importance
Slide 3: IoT Device Categories
-
Wearables
-
Remote Monitoring Devices
-
Smart Hospital Equipment
-
Implantable Devices
Slide 4: Use Cases
-
Remote monitoring
-
Smart beds
-
Emergency response
-
Elderly care
-
Predictive analytics
Slide 5: Benefits
-
Real-time data
-
Automation
-
Reduced medical errors
Slide 6: Challenges / Risks
-
Security
-
Privacy
-
Interoperability
Slide 7: Future Trends
-
AI-powered diagnostics
-
Smart hospitals
-
5G in healthcare
-
Personalized medicine
Slide 8: Conclusion
-
Importance of IoT in transforming patient care
Internal Link Opportunity:
From this section, link to /iot-in-healthcare-ppt/ when updating your cluster.
Future Trends in Healthcare IoT
The IoT healthcare ecosystem continues to grow rapidly. Key emerging trends include:
AI + IoT (AIoT) in Medical Diagnosis
Artificial intelligence analyzes data collected by IoT devices to detect early signs of diseases.
5G-Enabled Medical Devices
Faster speeds and low latency improve remote surgeries, telemedicine, and high-resolution imaging.
Smart Hospitals 2.0
Hospitals will use IoT to automate almost everything—from patient tracking to predictive equipment maintenance.
Digital Therapeutics
IoT-powered apps and devices will play a major role in mental health management, chronic disease treatment, and rehabilitation.
FAQs About IoT in Healthcare
1. What are the key advantages of IoT in healthcare?
Better monitoring, early detection, automation, and improved patient outcomes.
2. Is IoT safe to use in hospitals?
Yes, when devices are secured with encryption, regular updates, and access control.
3. What skills are needed to work on IoT healthcare projects?
Embedded systems, cloud platforms, networking, security, and basic medical domain knowledge.
4. How is IoT used in remote patient monitoring?
Devices collect patient data and send it to doctors in real time through cloud platforms.
5. Will IoT become essential in all hospitals?
Most global healthcare systems are already moving toward fully connected, smart hospital models.